SWOT Analysis
A scan of the internal and external environment is an important part of the strategic planning process. Environmental factors internal to the firm usually can be classified as strengths (S) or weaknesses (W), and those external to the firm can be classified as opportunities (O) or threats (T). Such an analysis of the strategic environment is referred to as a SWOT analysis.
The SWOT analysis provides information that is helpful in matching the firm’s resources and capabilities to the competitive environment in which it operates. As such, it is instrumental in strategy formulation and selection.
SWOT Analysis Framework
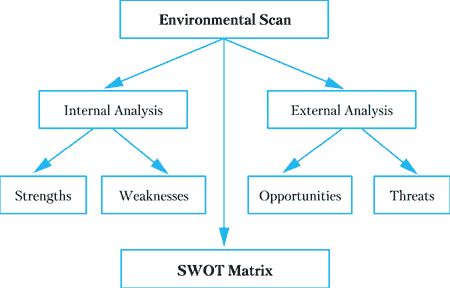
Strengths. A firm’s strengths are its resources and capabilities that can be used as a basis for developing a competitive advantage. Examples of such strengths include:
– patents or certain expertise;
– strong brand names;
– good reputation among customers;
– cost advantages from proprietary know-how;
– exclusive access to high grade natural resources;
– favorable access to distribution networks.
Weaknesses. The absence of certain strengths may be viewed as a weakness. For example, each of the following may be considered weaknesses:
– lack of patent protection;
– a weak brand name;
– poor reputation among customers;
– high cost structure;
– lack of access to the best natural resources;
– lack of access to key distribution channels.
In some cases, a weakness may be the flip side of a strength. Take the case in which a firm has a large amount of manufacturing capacity. While this capacity may be considered a strength that competitors do not share, it also may be considered a weakness if the large investment in manufacturing capacity prevents the firm from reacting quickly to changes in the strategic environment.
Opportunities. The external environmental analysis may reveal certain new opportunities for profit and growth. Examples of such opportunities include:
– an unfulfilled customer need;
– arrival of new technologies;
– loosening of regulations;
– removal of international trade barriers.
Threats. Changes in the external environment also may present threats to the firm. Examples of such threats include:
– shift in consumer tastes away from the firm’s products;
– emergence of substitute products;
– new regulations;
– increased trade barriers.
Более 800 000 книг и аудиокниг! 📚
Получи 2 месяца Литрес Подписки в подарок и наслаждайся неограниченным чтением
ПОЛУЧИТЬ ПОДАРОКДанный текст является ознакомительным фрагментом.